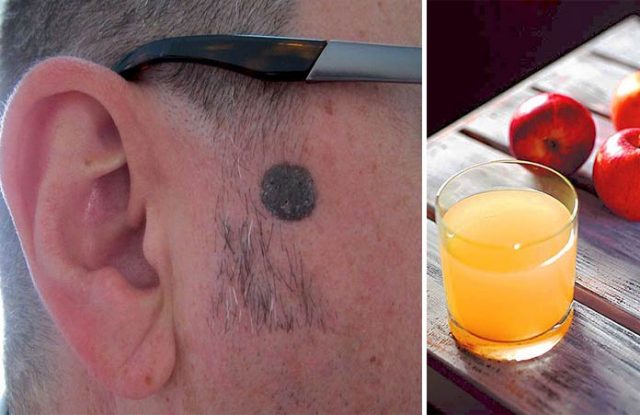
A beauty spot is a mole on the chin that can brighten one’s face and look attractive. However, all moles are not called as beauty spots. Some moles can get so large that their obtrusive appearance can look unsightly and ugly at times. Some moles can get so large having hair growth that they are often jokingly referred to as the symbiotic twin.
Large moles on the face are not pleasing to the eyes. Very often they take away the attention from the person’s face. People inadvertently stare at the odd growth than the persons face or features. Many fairy tales and stories represent witches and villains with large moles, which is far from the truth. A mole is not painful but can cause immense pain and psychological distress to a person having them.
Most people start getting moles by the age of 9 and they continue to grow until their late twenties. An average person can have anywhere from 20-25 moles on the body. Moles can begin to accumulate, clump or spread.
What is the composition of a mole?
Moles are a collection of pigment-producing cells that reside on the top layer of the skin. They are usually dark brown, light brown, blue, red (cherry angioma) or black in color. They are a natural process of skin development influenced by genes or exposure. They are living cells that can grow and change with time.
Melanocytes are cells that give the skin its color or pigmentation. When melanocytes begin to concentrate and accumulate in one spot they become moles. Moles begin to develop during teens years. Women tend to see more pigment changes during pregnancy due to overactive hormones. Moles darken with exposure to the sun.
There are 2 types of moles:
Congenital Nevi
Congenital Nevi moles are present at birth. They are the moles a person is born with. These moles have a small chance of developing into melanoma (skin cancer). Any birthmark bigger than 2 inches in diameter must be checked out by a doctor.
Dysplastic Nevi
Dysplastic moles are usually bigger than 2 inches in diameter, irregular in shape and are unevenly pigmented. They are usually dark on the center and fade towards the edges. These moles have a slightly higher chance of developing into melanoma. People with 10 or more Dysplastic Nevi moles have a 10 percent higher chance of developing skin cancer a serious skin condition. Any changes in the moles must be checked out by the doctor immediately.
What is cherry angioma? How is a cherry angioma different from a regular mole?
Cherry angiomas are accumulation and growth of blood vessels underneath the skin, unlike moles that are a concentration of melanin. Cherry angiomas get their name from their red appearance on the skin. They carry blood vessel in them and hence are red in color. Cherry angiomas are also referred to as senile angiomas or Campbell de Morgan spots. These lumpy growths usually tend to show up from the age of 30. Usually, they are not a cause for concern. However, if the growth begins to get larger, bleed from time to time with a gentle rub or friction, the color of the blood is unusually brown or red, it must be seen by a dermatologist immediately.
Cherry angiomas are often bright red, circular or oval in shape. While some look raised, others look smooth. They are mostly found in the covered areas the torso, arms, and shoulders.
Causes of Cherry Angioma:
The causes of Cherry Angioma are not exactly known. However, exposure to certain kinds of chemicals, climates, medicines, and pregnancy have known to cause them.
Procedure for remove Cherry Angioma
- Shave excision – Shaving off the region. Unlike mole removal, sutures are required after cutting of the lump as it carries blood vessels since they bleed profusely once they are cut.
- Laser surgery – A procedure of concentration of yellow laser lights is exposed to the lesion to destroy it. It is a quick outpatient procedure and does not require any cuts or stitches.
- Electrocauterization – A procedure where tiny probes are introduced into the lesion and destroyed giving mild electric current.
- Cryosurgery – An out-patient procedure that uses liquid nitrogen to freeze the lesion. The liquid is spread for about 10 seconds. The rest is left for the body to work. In a few hours the frozen lesion will begin to dry, and in a day or two form a scab and eventually fall off within a week or so of the procedure.
Causes of moles
- Hereditary- Moles have a genetic component. It is not uncommon to find the child with the similar birthmark as the parent.
- Age – While some people are born with moles, other develop them over time as they age.
- Sun exposure- People with excessive sun exposure like sunbathing and tanning can develop dysplastic Nevi moles.
Prevention of moles
- While nothing can be done to prevent the natural congenital Nevi, it is possible to prevent Dysplastic Nevi by wearing an SPF of 30 or more 30 minutes before stepping out in the sun.
- Wear hats with wide brims to prevent the sun rays from falling on the face.
- Wear a long-sleeved shirt and full pants or sun protective clothing before stepping out in the sun.
- Avoid stepping out during peak sun hours (12 – 4 pm) when the UV radiation is the strongest.
- Carry an umbrella when you step out in the sun.
- Stay indoors if you don’t need to be out.
- Get larger and newer moles checked out regularly.
- Avoid sun tanning for longer than 45 minutes.
- Avoid UV beds and tanning lamps as they increase the risk of moles and melanoma.
- Get your moles checked out and possibly get rid of them if they are growing to be too large.
ABCDE mole diagnoses
It is certainly not a good idea to use apple cider vinegar on a cancerous mole. Home treatment of the mole must be done only after a doctor’s careful ABCDE diagnosis to ascertain if it is benign or cancerous. The ABCDE method stands for the following:
- A: Asymmetry – The doctor will examine the mole to see if it is asymmetrical.
- B: Border – If the mole has fuzzy borders it will need to be examined further.
- C: Color – If the mole is not uniformly pigmented, further investigation is needed.
- D: Diameter- Mole bigger than two inches in diameter is cause for concern.
- E – Evolving – Mole that is evolving and getting bigger must be addressed right away and procedurally removed if possible.
Procedure for removing moles
The dermatologist can use any one or more procedures to remove a raised mole.
- Cutting the protruding mole
- Scraping the extruding mole with help of a scalpel blade.
(Both these procedures do not require stitches.) - Laser removal- This method is slow and usually involves many sittings. Also, laser removal does not penetrate deep into the skin, so a 100 percent removal of the mole is usually not possible.
A mole on scalp removal is even more obvious and cumbersome as it involves shaving off a part of your hair. Mole removal or scraping is a painful and expensive procedure. Very often moles require several sittings which could put a deep hole in your pockets.
Alternatively, people have tried natural and safer remedies for mole removal. Apple cider vinegar removal has proven to be very effective for many. So why not start with apple cider vinegar before you try other expensive painful procedures?
Do home remedies for moles work?
Yes! By far, using apple cider vinegar for moles is becoming a popular DIY mole removal remedy. Apple cider vinegar is known as a powerful antibacterial and antifungal agent with powerful healing properties. It also makes a great cleaning and bug-repelling solution. But did you know that Apple cider vinegar also works wonders in lighting the skin tone and naturally removing moles? Apple cider vinegar flat mole removal is safe and effective and can be done at home.
The natural tannins and acetic acids present in apple cider vinegar, when applied on warts and moles, penetrate deep into the skin and dry the top layer. A mild burning sensation is experienced which is quite normal due to the burning action of the acid. However, if the burning sensation is unbearable or you develop a pain in the region or fever stop immediately and consult your dermatologist. With regular application, it eventually turns into a scab and falls out. Under no circumstance should the scab be pulled out. Wait for the scab to dry out and fall naturally.
Why ACV for mole removal?
- It is least intrusive
- ACV is natural
- Has no side effects
- No bruising, cutting or scraping is involved
- Pain-free
- The easiest way to eliminate a mole from your face and body at home.
How to remove a mole at home?
Materials required:
- Pure apple cider vinegar
- Vaseline
- Cue tip
- Eyebrow tweezers
- Small cotton balls
- Bandages
How to use ACV to get rid of moles and cherry angioma at home?
This procedure must be done tactfully and carefully. Apple cider vinegar is acidic. It can dry out and burn the skin surface. To try a mole removal, follow the steps given below carefully:
- Take a cue tip and dip it in Vaseline.
- Gently rub the cue tip on the skin surface surrounding the mole so it is not affected by the ACV acid.
- Make a small ball of cotton, the size of your mole.
- Hold it with a pair of tweezers and dip it in ACV.
- Squeeze out the excess liquid to avoid dropping on the skin.
- Gently place it on the mole.
- Cover it with a bandage.
- Let the liquid deep into the skin overnight.
- Wash and clean the mole in the morning.
- Repeat the same procedure every night.
- Follow the pattern for 8-10 days.
In 2-3 days you will start to see your mole lighting and beginning to dry out. The size will begin to flatten and shrink. In 4-5 days, it will start turning into a scab. You may be tempted to pick the drying scab. Don’t do it as it could bleed. Wait for the mole to completely dry out, turn into a scab and naturally fall off. Once the scab falls off, it leaves behind a raw pink mole scar. This area will be sensitive for a few days as it is freshly exposed to the sun. Moisturize the area an apply an SPF 30 or higher on the spot before you leave home or step out into the sun. Gradually your skin tone will get its natural color and heal completely from the natural acid burn.
A note of caution: ACV for removal of moles and cherry angioma at home is meant only for non-malignant growths. Malignant or cancerous ones must be handled by the doctor exclusively. Get your mole or lesion checked out by a dermatologist before you start self-administering apple cider vinegar at home.